Welding is a complex and multifaceted field that requires a deep understanding of various principles and applications. As a fundamental process in manufacturing, construction, and repair, welding has numerous benefits and uses across different industries. In this article, we will delve into the world of welding, exploring its principles, applications, and the importance of mastering this skill.
Understanding the Basics of Welding
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion. This process is used to create a strong and permanent bond between two or more metal pieces, making it a crucial technique in various industries.
There are several types of welding, including:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
- Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Each type of welding has its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.
Welding Principles
To master welding, it is essential to understand the underlying principles that govern the process. These principles include:
- Heat Input: The amount of heat energy transferred to the workpiece during welding.
- Cooling Rate: The rate at which the weld cools, affecting the microstructure and properties of the weld.
- Welding Current: The flow of electric current used to generate heat during welding.
- Arc Voltage: The voltage across the welding arc, influencing the heat input and weld penetration.
Understanding these principles enables welders to optimize their techniques, ensuring high-quality welds and minimizing defects.
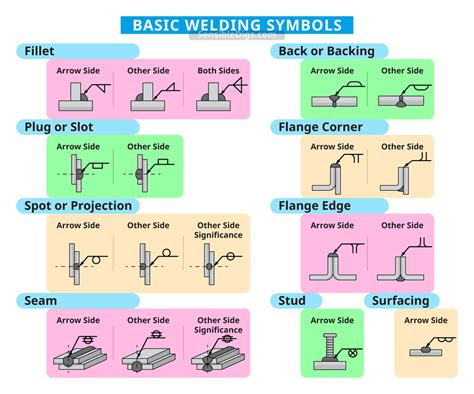
Applications of Welding
Welding has numerous applications across various industries, including:
- Construction: Welding is used in building bridges, high-rise buildings, and other infrastructure projects.
- Automotive: Welding is used in manufacturing cars, trucks, and other vehicles.
- Aerospace: Welding is used in building aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles.
- Shipbuilding: Welding is used in constructing ships and submarines.
- Piping: Welding is used in installing pipelines for oil, gas, and water.
Welding is also used in various repair and maintenance applications, such as fixing machinery, equipment, and tools.
Mastering Welding Techniques
To become a skilled welder, it is essential to master various techniques, including:
- Welding Positions: Welding can be performed in different positions, such as flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead.
- Welding Joints: Welding involves joining two or more metal pieces at a joint, which can be a butt joint, lap joint, or corner joint.
- Welding Processes: Welding involves various processes, such as shielded metal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, and gas tungsten arc welding.
Mastering these techniques requires practice, patience, and dedication.

Safety Precautions in Welding
Welding involves working with high temperatures, sparks, and hazardous materials, making safety precautions essential. Some of the safety precautions include:
- Personal Protective Equipment: Welders should wear personal protective equipment, such as helmets, gloves, and safety glasses.
- Ventilation: Welding areas should be well-ventilated to prevent inhaling fumes and particles.
- Fire Prevention: Welding areas should be kept clean and free of flammable materials.
Following safety precautions ensures a safe working environment and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Conclusion
Mastering welding principles and applications is crucial for anyone involved in this field. By understanding the underlying principles, techniques, and safety precautions, welders can produce high-quality welds and minimize defects. Whether you are a novice or an experienced welder, continuous learning and practice are essential to stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and technologies.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of welding. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.





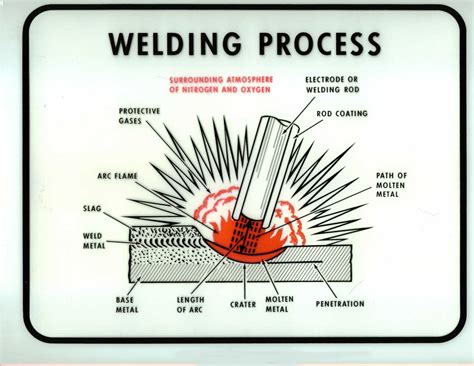
What is welding?
+Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion.
What are the different types of welding?
+There are several types of welding, including Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), and Submerged Arc Welding (SAW).
What are the safety precautions in welding?
+Some of the safety precautions in welding include wearing personal protective equipment, ensuring good ventilation, and preventing fires.
