Welding is a complex process that requires patience, practice, and attention to detail. For beginners, understanding the fundamental principles of welding is crucial to produce high-quality welds and ensure safety. In this article, we will explore the 9 essential welding principles for beginners, providing a comprehensive guide to get you started on your welding journey.
1. Safety First: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)

Before starting any welding project, it's essential to wear the proper personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes a welding helmet, safety glasses, gloves, and a fire-resistant jacket. PPE protects you from the intense heat, sparks, and UV radiation emitted during the welding process.
Key Safety Considerations:
- Always wear a welding helmet with a shaded lens to protect your eyes from UV radiation.
- Use safety glasses with a side shield to protect your eyes from sparks and debris.
- Wear heat-resistant gloves to protect your hands from burns and cuts.
- Wear a fire-resistant jacket and pants to protect your skin from sparks and flames.
2. Choosing the Right Welding Process
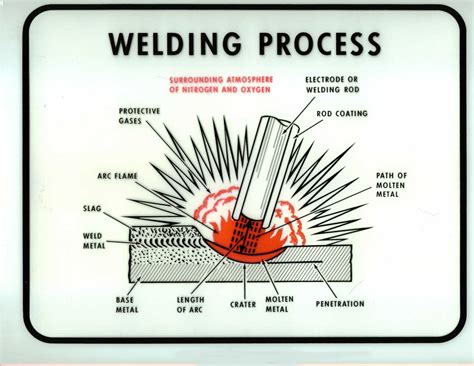
There are several welding processes, including Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). Each process has its own advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one depends on the specific project requirements.
Common Welding Processes:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as "stick" welding, this process uses a consumable electrode covered in flux to protect the arc.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): Also known as "MIG" welding, this process uses a continuous wire electrode and an inert gas to shield the arc.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): Also known as "TIG" welding, this process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas to shield the arc.
3. Selecting the Right Welding Electrode

The welding electrode is a critical component of the welding process. It must be compatible with the base metal and the welding process being used. There are several types of welding electrodes, including consumable and non-consumable electrodes.
Types of Welding Electrodes:
- Consumable electrodes: These electrodes are designed to melt and become part of the weld. Examples include SMAW and GMAW electrodes.
- Non-consumable electrodes: These electrodes are designed to withstand the high temperatures of the welding process without melting. Examples include GTAW electrodes.
4. Setting Up Your Welding Station

A well-organized welding station is essential for efficient and safe welding. This includes setting up your welding machine, electrode holder, and workbench.
Key Components of a Welding Station:
- Welding machine: This is the power source for your welding process.
- Electrode holder: This is used to hold the welding electrode in place.
- Workbench: This is the surface where you will be welding.
5. Preparing the Base Metal

Before welding, it's essential to prepare the base metal. This includes cleaning the metal to remove dirt, oil, and other contaminants.
Importance of Base Metal Preparation:
- Ensures a strong bond between the base metal and the weld.
- Prevents porosity and other defects in the weld.
- Improves the overall quality of the weld.
6. Maintaining Proper Welding Technique

Proper welding technique is critical to producing high-quality welds. This includes maintaining the correct arc length, electrode angle, and travel speed.
Key Elements of Proper Welding Technique:
- Arc length: This is the distance between the electrode and the base metal.
- Electrode angle: This is the angle at which the electrode is held relative to the base metal.
- Travel speed: This is the speed at which the electrode is moved along the joint.
7. Controlling Heat Input

Heat input is a critical factor in welding. Too much heat can cause distortion, porosity, and other defects. Too little heat can result in a weak bond.
Importance of Heat Input Control:
- Ensures a strong bond between the base metal and the weld.
- Prevents distortion and other defects in the weld.
- Improves the overall quality of the weld.
8. Monitoring Weld Quality

Monitoring weld quality is essential to ensuring that the weld meets the required standards. This includes visual inspection, non-destructive testing, and destructive testing.
Methods of Weld Quality Monitoring:
- Visual inspection: This involves visually inspecting the weld for defects and imperfections.
- Non-destructive testing: This includes methods such as radiography, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle testing.
- Destructive testing: This includes methods such as tensile testing and bend testing.
9. Practicing Welding Safety

Welding safety is critical to preventing injuries and ensuring a safe working environment. This includes following proper safety procedures, wearing personal protective equipment, and maintaining a clean and organized workspace.
Importance of Welding Safety:
- Prevents injuries and fatalities in the workplace.
- Ensures a safe working environment.
- Improves overall productivity and efficiency.






What is the most important safety consideration in welding?
+The most important safety consideration in welding is wearing proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including a welding helmet, safety glasses, gloves, and a fire-resistant jacket.
What is the difference between SMAW, GMAW, and GTAW welding processes?
+SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) uses a consumable electrode covered in flux, GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding) uses a continuous wire electrode and an inert gas, and GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas.
What is the importance of heat input control in welding?
+Heat input control is critical to preventing distortion, porosity, and other defects in the weld. It ensures a strong bond between the base metal and the weld.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the 9 essential welding principles for beginners. Remember to always follow proper safety procedures, choose the right welding process and electrode, and maintain proper welding technique to produce high-quality welds.
